Easy Deep Learning on AWS with MindsEye
Let’s say you have a local java application you are developing. For some reason, you want to run some code on AWS EC2 - After all, the cloud and virtual computing revolution makes all that theoretically easy. All you need is an AWS account… right?
However, if you are starting from a local Java application and just have the goal “run this code on the cloud”, there are actually quite a few problems to solve before you can do this. You must configure security policies, SSH keys, and roles, then start ec2 instances, then deploy code, then somehow start a process, and finally somehow interact with your child process.
Although many solutions exist for many of these problems, there is no single simple solution on parity with local execution. Because of the amount of plumbing needed, there is a strong barrier between the components of an application base on where they are physically located. That is one of the coolest features of Apache Spark - it lowers this inter-process barrier and makes it easy to program a cluster of machines using lambdas.
The latest component I’ve developed is an AWS utility library that makes it convenient to bootstrap slave JVMs on new EC2 instances with a very simple process. It is designed to be simple enough for new users, yet secure and performant and scalable enough for use in production systems; I intend to use this to both support research and provide Machine-Learning-as-a-Service capabilities.
For a simple example, see this demonstration code. It demonstrates the basics of setting up an AWS Node and invoking lambdas on it; this is now not much harder than local execution via a threadpool!
This adds easy access to cloud computing facilities, such as Amazon’s Deep Learning machine images which we can use to execute MindsEye Art scripts. Using the notebook logging api, we easily produce reports in markdown, html, and pdf as well as providing interactive http endpoints. This is demonstrated in the following applications, which can be executed in local or AWS mode:
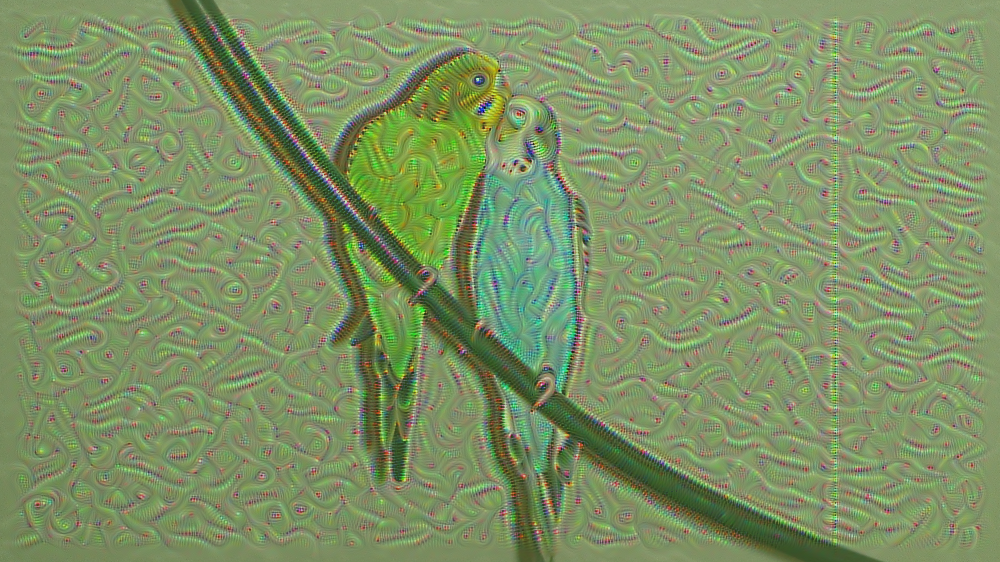
Deep Dream - This process enhances latent patterns within an input image.
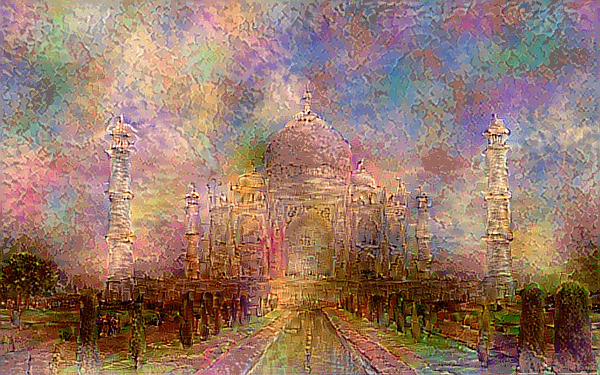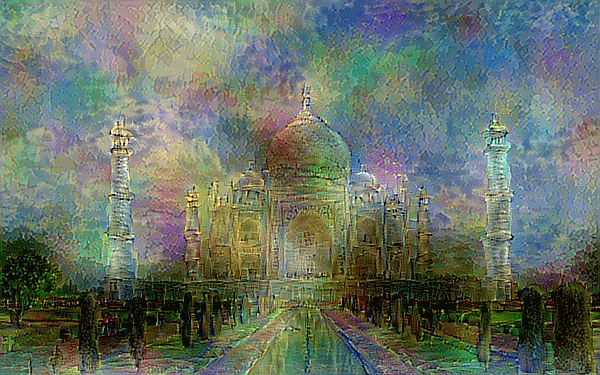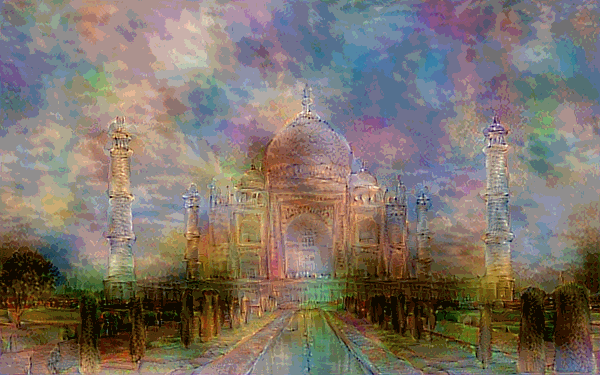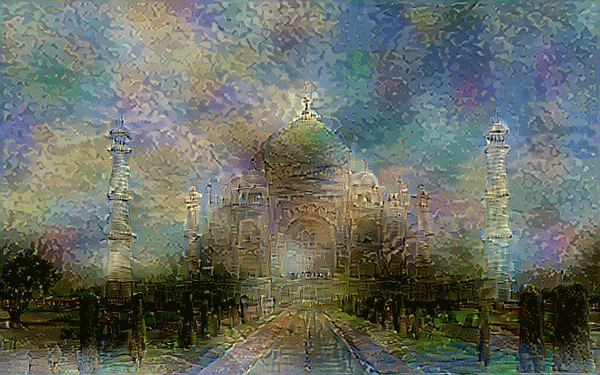
Style Transfer - This combines two images, using the content of one image and the style of another to render a unique combination of the two.
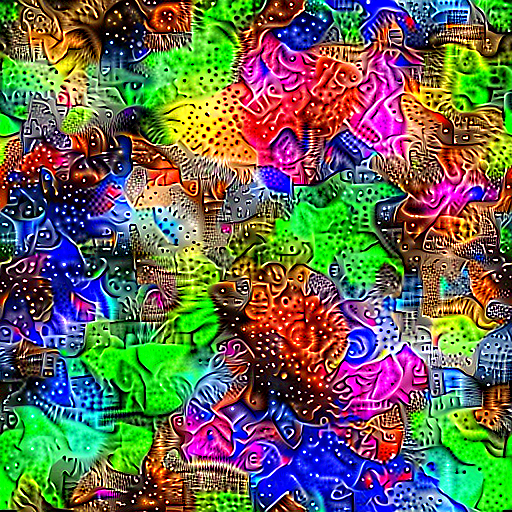

Texture Generation - Very similar to style transfer, this process lacks a content image and thus generates abstract imagery.
Each script, when run in remote mode, will use the default AWS credentials (your environment-supplied credential) to bootstrap an AWS EC2 instance to run the report in question. This report will then be archived in S3, and the instance cleaned up. This provides any consumer with access to either recent NVidia GPUs or AWS to run these scripts and generate their own Deep Learning Art!
How does this tool work? What does it do? First, it supplies some logic to create, if needed, a variety of required AWS entities, allowing the user to focus on using an EC2 instance instead of creating and configuring it. As part of this automatic configuration, it produces SSH keys which are then used with the JSch library to provide a simple api to execute commands. This execution api is used to manage a transfer of the entire current classpath to the remote service, using hashing and S3 to improve efficiency. We then bootstrap a remove JVM process which runs an RMI server using Kryonet, and we connect to that service using an SSH tunnel. We then initialize a client for this remote node management endpoint, and return it. This client can then be used directly to execute lambdas on the remote machine. When we are finished with this execution, we can easily clean up our node by closing the node eternally or exiting the process internally.
We are left with a super-simple way to run code on AWS. Enjoy!
